Table of Contents

[/image][=video]
[/video]
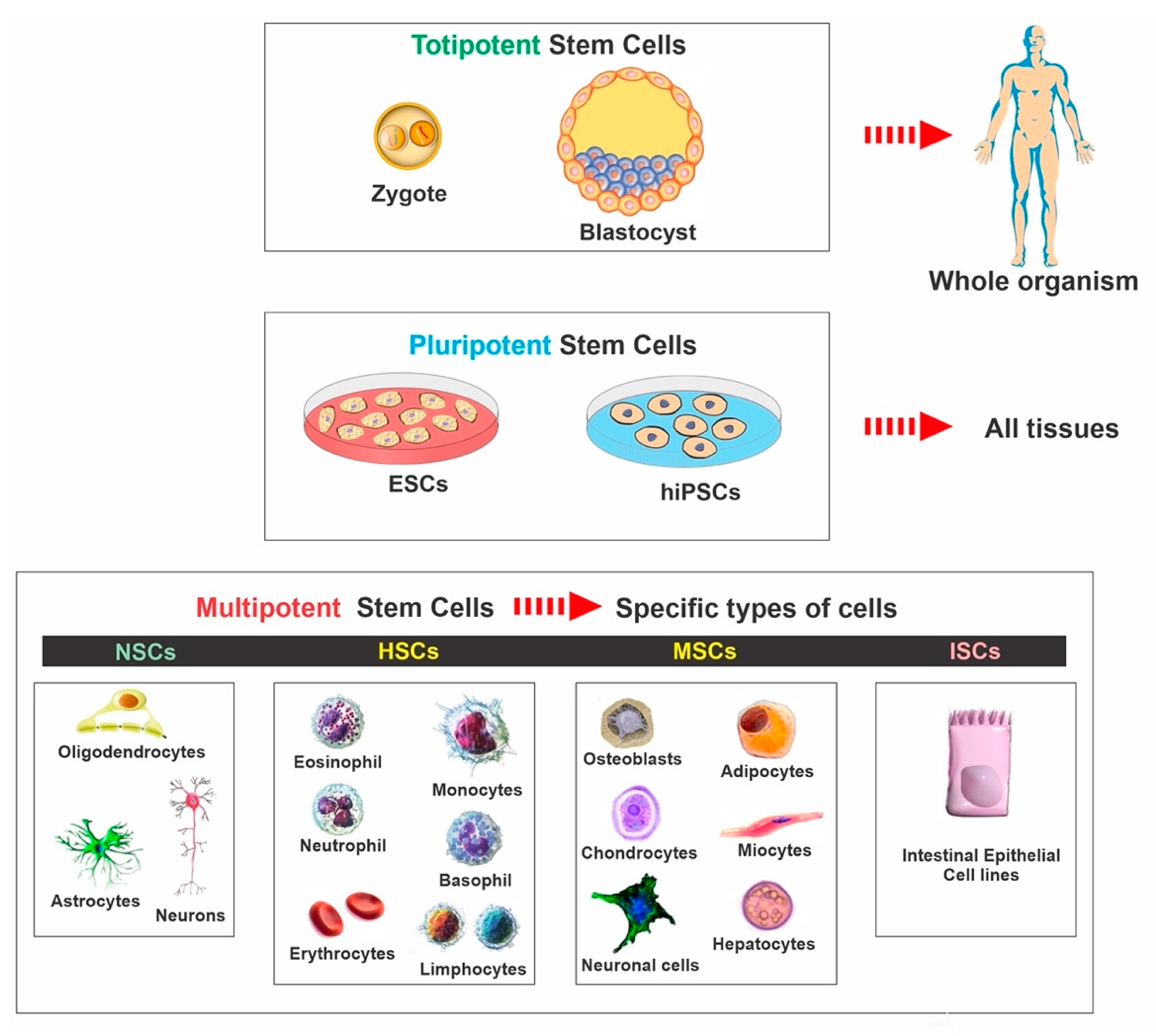
There are several types of stem cells. As a whole, the term stem cell describes a category of cells that generate other cells (like skin, blood, heart, and muscular tissue cells) by reproducing and differentiating in response to chemical cues. Totipotent stem cells show up at the earliest stage of development and are the only stem cells which can produce embryonic stem cells and the placenta.
Bone marrow transplant (BMT) is a special treatment for people with particular cancers cells or other diseases. A bone marrow transplant involves taking cells that are usually located in the bone marrow (stem cells), filtering system those cells, and giving them back either to the benefactor (patient) or to another person. The objective of BMT is to transfuse healthy bone marrow cells right into an individual after his or her own undesirable bone marrow has been treated to eliminate the abnormal cells.
Bone marrow is the soft, mushy tissue located inside bones. It is where the majority of the body's blood cells create and are kept. The blood cells that make various other blood cells are called stem cells. One of the most primitive of the stem cells is called the pluripotent stem cell. This is different than other blood cells when it come to the following properties: It has the ability to duplicate an additional cell identical to itself.
It is the stem cells that are required in bone marrow transplant. The objective of a bone marrow transplant is to cure many illness and types of cancer. When the doses of radiation treatment or radiation required to cure a cancer are so high that an individual's bone marrow stem cells will certainly be permanently damaged or destroyed by the therapy, a bone marrow transplant might be needed.
Stem Cell Therapy around Grand Rapids, Michigan
This process is commonly called rescue. Change bone marrow with genetically healthy operating bone marrow to avoid even more damages from a hereditary condition process (such as Hurler's disorder and adrenoleukodystrophy). The risks and advantages must be considered in an extensive discussion with your doctor and specialists in bone marrow transplants before the treatment.
There are different sorts of bone marrow transplants relying on that the benefactor is. The different kinds of BMT include the following: The donor is the individual himself or herself. Stem cells are taken from the individual either by bone marrow harvest or apheresis (a process of accumulating outer blood stem cells), icy, and after that returned to the client after intensive therapy.
The benefactor shares the same hereditary kind as the patient. Stem cells are taken either by bone marrow harvest or apheresis from a genetically matched donor, normally a sibling or sister. Other donors for allogeneic bone marrow transplants may include the following: A haploid-identical suit is when the donor is a parent and the genetic suit is at least half identical to the recipient.

Matching includes keying human leukocyte antigen (HLA) cells. The antigens externally of these special white blood cells identify the hereditary makeup of an individual's body immune system. There are at least 100 HLA antigens; nonetheless, it is thought that there are a couple of significant antigens that establish whether a contributor and recipient suit.
Clinical research is still investigating the function all antigens play in the process of a bone marrow transplant. The even more antigens that match, the better the engraftment of given away marrow. Engraftment of the stem cells happens when the contributed cells make their method to the marrow and start making new blood cells.
Medical Group in Grand Rapids, Michigan
All individuals work together to provide the ideal chance for a successful transplant. The team consists of the following: Medical care suppliers who specialize in oncology, hematology, immunology, and bone marrow transplantation.
Professionals that will assist you fulfill your dietary needs before and after the transplant. Numerous various other team members will assess you prior to transplantation and will give follow-up treatment as needed.
A complete case history and physical exam are carried out, consisting of several tests to assess the patient's blood and body organ functions (as an example, heart, kidney, liver, and lungs). A person will frequently enter into the transplant center as much as 10 days prior to transplant for hydration, examination, positioning of the main venous line, and various other preparations.
Blood products and medicines will certainly be offered via the catheter throughout therapy. For an allogeneic transplant, an appropriate (cells entered and matched) benefactor has to be offered. Finding a matching donor can be a difficult and lengthy procedure, especially if a sibling match is not readily available. Voluntary marrow contributors are registered in several nationwide and worldwide computer registries.
Contributor resources readily available include: self, sibling, parent or family member, nonrelated individual, or umbilical cord from a relevant or nonrelated person. There are nationwide and worldwide windows registries for nonrelated individuals and cable blood. Some member of the family might be typed as a result of the wish to aid. These relatives might or might not choose to have their type registered for use with other receivers.
Perimenopause Treatment
Tests connected to his/her health, direct exposure to infections, and genetic analysis will be done to determine the level of the suit. The benefactor will be offered directions on exactly how a bone marrow donation will be made. When a match for a patient needing a bone marrow transplant is found, then stem cells will be gathered either by a bone marrow harvest.
Or by a peripheral blood stem cell collection. This is where stem cells are collected from the circulating cells in the blood.
Navigation
Latest Posts
Regenerative Therapy
Perimenopause Treatment in Grand Rapids
Regenerative Therapy local to Grand Rapids